 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
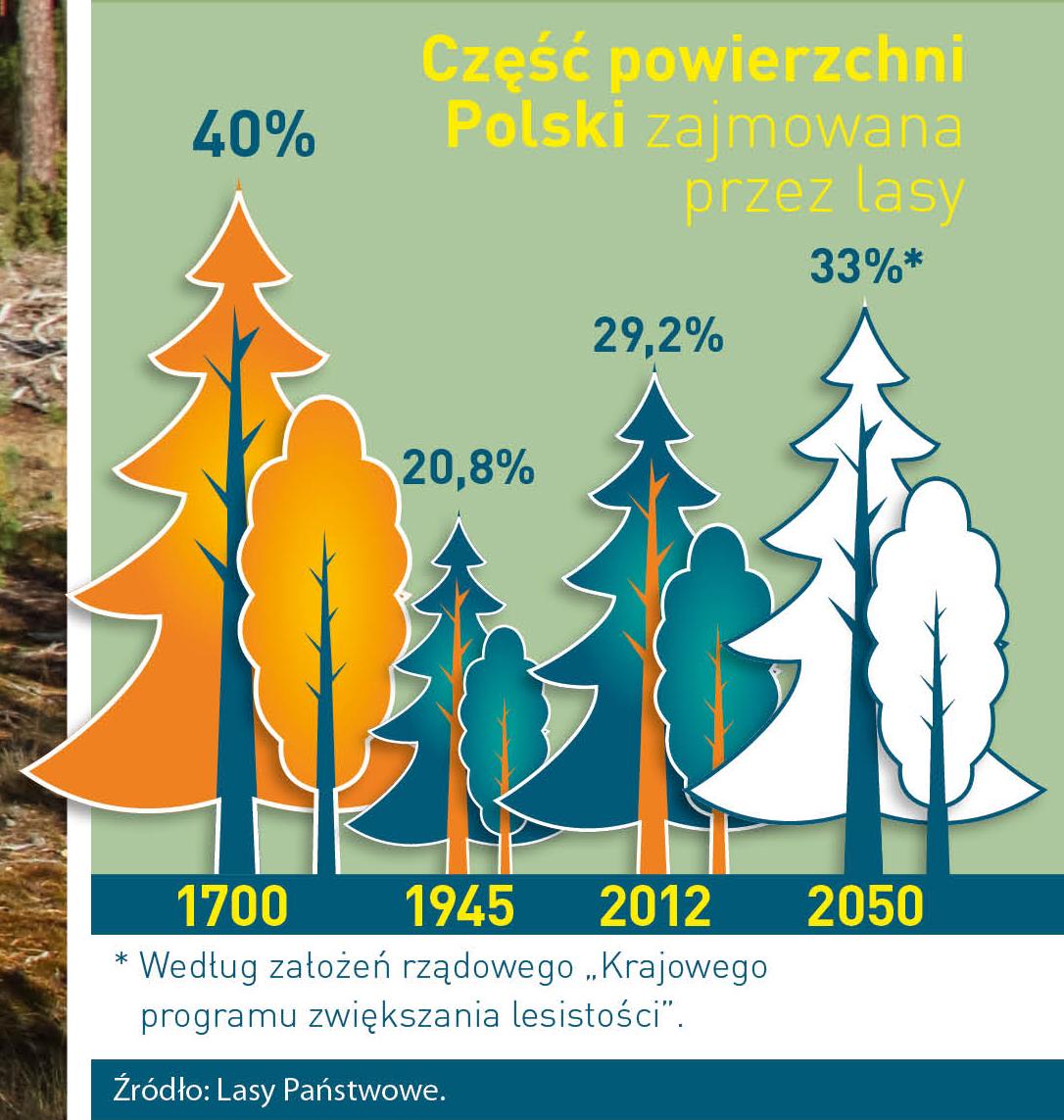
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Dowiedz się więcej o wieżach przeciwpożarowych?
Dowiedz się więcej o wieżach przeciwpożarowych?
Wieża obserwacyjna to sztucznie wzniesiony punkt widokowy usytuowany przeważnie w najwyższym miejscu w terenie umożliwiający oglądanie panoramy otaczającego krajobrazu. Obiekt zaliczany jest do rozległego sytemu przeciwpożarowego. Wieże mają za zadanie wczesne wykrycie pożaru oraz zawiadomienie o jego powstaniu. Można z nich obserwować teren w promieniu, co najmniej 10 km. Obszar, który widoczny jest z jednej wieży, nakłada się na teren dostrzegalny z drugiej wieży, co pozwala na wyznaczenie dokładnego miejsca powstania pożaru. Obserwatorzy podają do Punktu Alarmowo Dyspozycyjnego (PAD) namiary kątowe zauważonego dymu. Dane odczytuje się za pomocą kolimatora. Objętość obłoku powstającego przy pożarze o powierzchni około 100m2 wystarczy, aby z dostrzegalni zauważyć i określić położenie pożaru. Wszystkie meldunki obserwator składa drogą radiową lub telefoniczną.
W Nadleśnictwie Karwin usytuowane są dwie wieże obserwacyjne. Jedna znajduje się w Leśnictwie Wilcze Doły, a druga w Leśnictwie Lipki Wielkie.
Wieża obserwacyjna w Leśnictwie Wilcze Doły posiada konstrukcję stalową, kratową i wznosi się na wysokość 32m. Aby wejść na szczyt obiektu należy pokonać aż sto piętnaście schodów, które rozdzielone są ośmioma podestami spoczynkowymi. Na szczycie znajduje się kabina obserwatora obudowana z oknami. Z kabiny można wyjść na podest obserwacyjny. Wieża w ramach wzmocnienia została wyposażona w odciągi linowe mocowane parami w trzech kierunkach.
Wieża obserwacyjna w Leśnictwie Lipki Wielkie ma konstrukcję żelbetową. Wznosi się na wysokość 32m. Na szczycie umiejscowiona jest kabina służąca obserwacji obszarów leśnych, która jest w kształcie wieloboku (ośmiokąta). W jednej z jej ścian umieszczone są drzwi umożliwiające wyjście na podest obserwacyjny, który jest konstrukcji stalowej. Podest ma szerokość 70 cm i posiada specjalną balustradę. Do stalowej konstrukcji pomieszczenia obserwacyjnego zamontowany jest wspornik z rolką, który ma za zadanie umożliwić ewakuację obserwatora, a także transport posiłków i napojów. Na samym dole wieży znajduje się otwór wejściowy o wymiarach 80x200 cm. Na dwunastu poziomach od strony południowej znajdują się otwory okienne z siatkami. Wieża wyposażona jest w ciągi komunikacyjne, czyli klatkę schodową oraz spoczynki.
Dostrzegalnie nie są udostępniane dla ruchu turystycznego. Odgrywają nieocenioną rolę w walce z żywiołem.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 Wieża p-poż w Leśnictwie Lipki Wielkie
Wieża p-poż w Leśnictwie Lipki Wielkie
 Widok z wieży p-poż w Leśnictwie Wilcze Doły
Widok z wieży p-poż w Leśnictwie Wilcze Doły




